Previous …
上一次,我們講到 邏輯時間 ,可以幫助更新順序。這次,我們談到另一個時間。
Last time, we discuss about logical clock which updates in the same order at all replicas. This time, we will discuss about another clock.
Causal ordering …
在分布式系統中,這是一個重要的觀念。我們通常以事件發生順序來做總排序。意思是,現在有多台機器,A -> B 代表 A 發生在 B 之前。以先前的寫法即 C(A) < C(B)。 B -> C,則 B 發生在 C 之前。如此可以推斷 A -> C。
This is an important rule concept in distributed system. We usually order events by when event happened. Now, there are several machines and A -> B represents A happened before B. In previous format, we can also write C(A) < C(B). B -> C which means B happened before C. In this case, we can infer that A -> C.
Vector clock …
1.
向量時間用來確認事件是否是因果排序。
Vector Clocks determine whether events are causally related.
2.
每一個執行序有自己的向量值。
It has its own value of each process.
Example: there are three processes. The vector clock represent [c0,c1,c2] = [0,0,0]
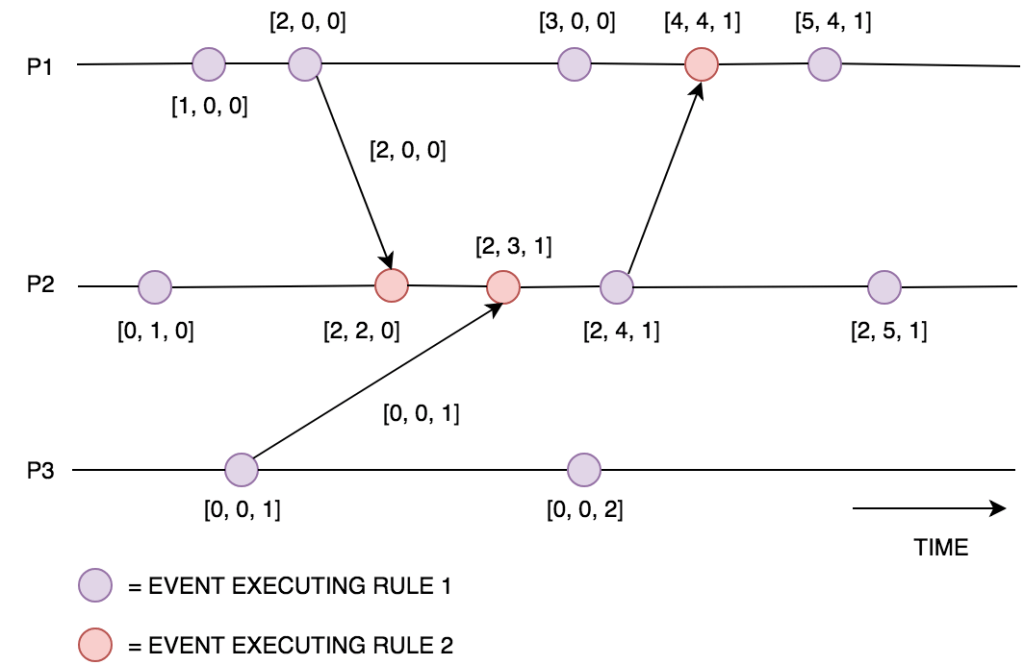
Executing rules …
1.
若事件發生在本地執行序,則更新自己的向量值。
For each local event, increment local value on each process.
2.
如果執行序 i 收到訊息 D 向量時間,則 每個向量值 = max(本地向量值,收到D的向量值)。最後將自己的向量值加一。
If process i received message with vector clock D, set local value ci = max(ci,di). Then increment local value.
Example: If process1 has its own vector clock [3,0,0], then it received vector clock D = [2,4,1].
C0 = max(3,0) = 3; C1 = max(0,4) = 4; C2 = max(0,1) = 1. So it got [3,4,1]. Finally, it increment local value. So the result is [4,4,1].
-MsHe