
Why Paxos appeared …
Primary-Backup 的架構中,需要所有的 backup 都回傳 ACK 訊息,才算是同步成功。這樣的方式,會產生兩個問題。
1.並不是每一台機器都正常運作,如果有一台機器連不到,怎麼容忍部分正確。
2.怎麼讓程序正常執行,而不會因為暫時連不到機器而被卡住。
In primary-backup, primary must receive ACK message from all backup to ensure synchronization. This way causes two problems.
1. Not every machine is functional. How to tolerance partition.
2. How to work functionally without blocking users if there is one machine unavailable.
Key idea of Paxos …
像通過法律需要半數的公民同意,如果一半的機器承諾可以執行更新,則達成共識。
Like passing laws need to get majority of citizens agreement, the consensus can be achieved if there are majority of replicas commit to update.
Paxos …
1.
現今在業界被廣泛使用。
Nowadays, it is widely used is industry.
2.
可以達成最終一致。這意味著,只要有同意的值,最終所有機器都會發現這個值。
Can reach the consistency eventually. It means if there is a value which is committed to be updated, all machines will eventually discover the value.
3.
因為只需要一半機器的承諾,是一個高度容忍錯誤的演算法。
Since it only needs half of machines commitment, it is a algorithm that highly tolerances faults.
Roles of Paxos …
- Proposers: 提出更新值。Proposes values.
- Acceptors: 更新者,如果該值被一半以上的機器接受。 Accept values which are committed to be updated by majority of acceptors.
- 每個 acceptor 必須記住三個值。 Every acceptor maintains three values.
- np: 最高被承諾要更新的提案值。 The highest proposal number which is promised to accept.
- na: 已經被接受的最高提案值。 The highest proposal number which is accepted.
- va: 已經被接受的值。 The value accepted.
- Leaners: 學習最後選出的更新值。Learn the chosen values.
每台機器可以擔任任何的角色,也可以擔任不只一種角色,例如:可以同時為 proposer 跟 learner。
Each machine can be play any role, even can play more than one role. For example, one machine can be both proposer and learner.
Process of Paxos
Prepared Phase
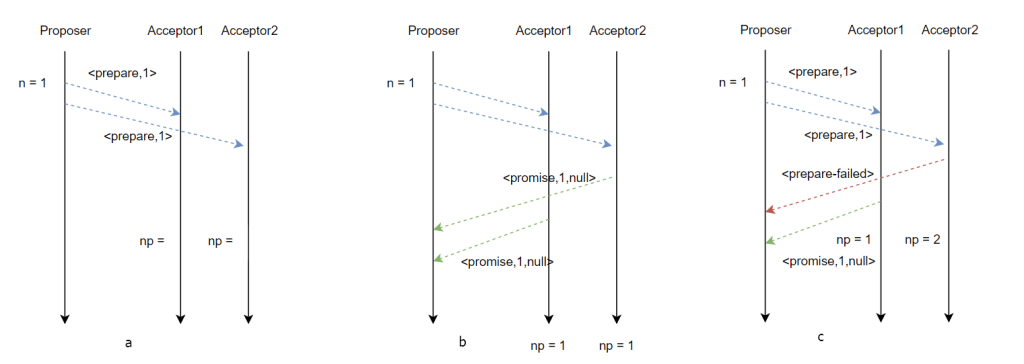
1.
提案者提出唯一的提案數 n。並且傳送 prepare 訊息給所有的接受者。(圖a)
Proposer proposes an unique proposal number n and sends prepare message to all acceptors. (Figure a)
2.
接收者接收到 prepare 訊息後,判斷是否收受提案。
After receiving prepare message, acceptor determine whether promise the propose.
If n > np
np = n
if there is no value accepted
sends promise message to proposer <promise,n,null> (Figure b)
if there is a value accepted
sends promise message to proposer <promise,n,(na,va)>
else
sends <prepare-failed> to proposer (Figure c)
Accept Phase
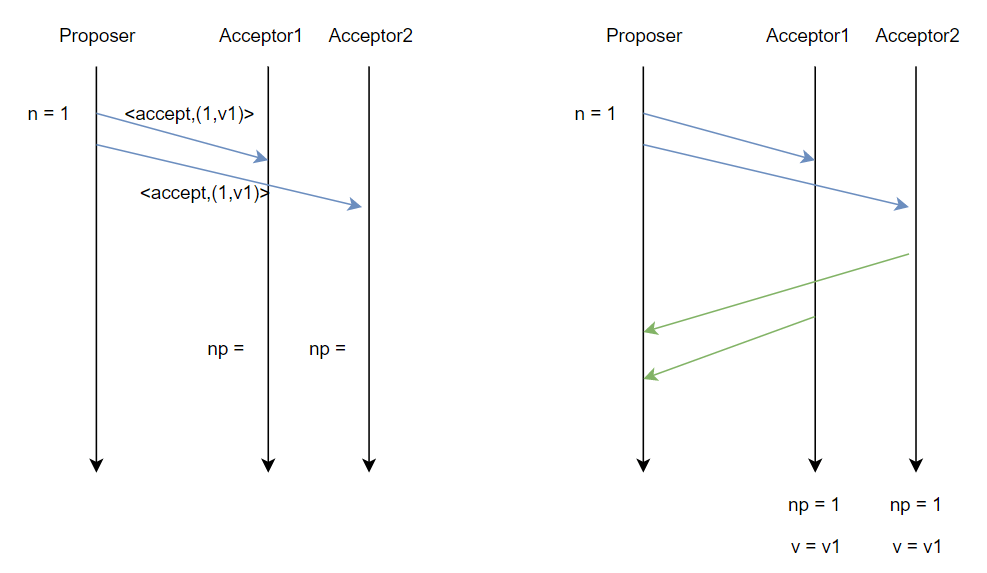
1.
一但提案者收到多數接受者承諾訊息後,傳送 <accept,(n,v)> 訊息給接受者。
Once proposer received promise message from majority of acceptors, it sends <accept,(n,v)> message to all acceptors.
‧ 如果 va 存在,則 v = va, 如果不存在,則 v = 自己的值。
‧ If va existed, then v = va, else v = its own value.
2.
接受者接受到訊息後 After acceptors receiving the message (Figure 2-a, 2-b)
n >= np (Figure 2-a)
na = np = n
va = v
Learner Phase
學習者發現被大多數接受者接受的值。
Learners discover the value which was accepted by majority of acceptors.
Questions …
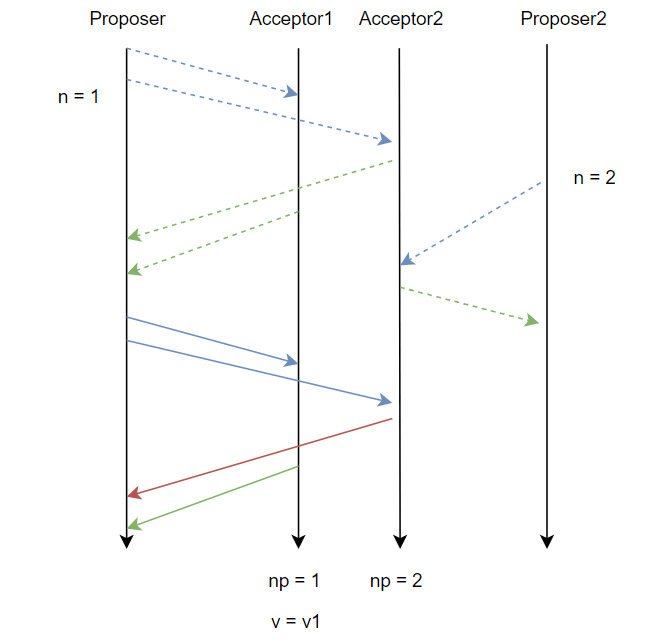
1.Like Figure 2-b, how to fix race condition?
當第二階段失敗後,不要馬上提出新的提案,先回到其他狀態。
When failed on second phase, don’t propose another proposal immediately and back off for a random period.
2. How do learners learn the value accepted?
利用第一階段的 prepare 訊息學習接受的值。
Learners discover value accepted by response of prepare message.
-MsHe